C C0 3 2-. Even though the C and O are connected by a single bond in one structure and a double bond in the other they are still connected to each other in both structures.

1 4 Diethylbenzene 1h Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase
In this text carboxylate groups will usually be drawn showing only one resonance contributor for the sake of simplicity but.
P-diethylbenzene number of resonance structures. These are resonance structures because they fulfill all three rules. Determine the number of possible resonance structures for BrO4-. With two resonance contributors to account for the equivalence of the two C-O bonds.
The existence of multiple resonance structures for aromatic hydrocarbons like benzene is often indicated by. There is no formula to find number of resonating structures but it is possible to do it manually. Dont get confused follow simple steps you can find it in your books too.
Number of carbon-hydrogen single C-H bonds. The structure contains two N-O single bonds and one NO double bond. The whole concept is qualitative so we cant draw any quantitative conclusions from it.
Number of major resonance structures. This is the kind of 3D picture that resonance contributors are used to approximate and once you get some practice you should be able to quickly visualize overlapping 2p z orbitals and delocalized pi electrons whenever you see resonance structures being used. Phenolate ion phenols conjugate base being stable by this resonance is a.
But if you want to do it anyway then of course 1 and 5 are the same while 2 and 4 are not they have positive charges on different atoms. Number of major resonance structures. Three resonance structures are necessary to account for the fact that the three C-O bonds in the carbonate anion are equivalent and these are shown below.
Determine the central atom in this molecule. The three resonance structures for dinitrogen monoxide are All the three resonance structures account for the 18 valence electrons and. However its measured structure is consistent with a description as a resonance hybrid of the two major contributing structures shown above.
The effect of resonance is the sharing of the double-bond. We will have to draw the Lewis Structure of BrO4- first. The N_2O molecule has a total number of 18 valence electrons - 6 from nitrogen and 6 from each oxygen atom.
In the same way that green does not change between blue and yellow a molecule does not shift from one resonance structure. Draw the Lewis Structure for the molecule. CH2 - CH3 Some facts about the p-diethylbenzene molecule.
CH2 - CH3 Some facts about the p-diethylbenzene molecule. Now draw a lewis structur. Calculate the total number of valence electrons present.
In VB terms the structure of benzene is a resonance hybrid of the two canonical structures. It is the easiest way that chemists can describe different contributions to the total picture of the hybrid molecule. Enter your search term above and find.
The existence of this resonance in phenolate ion provides it quite some stability hence phenol is acidic. Therefore three valid resonance structures can be drawn. Each atom has an octet in all three resonance structures.
In quantum mechanical terms the blending effect of resonance in the Lewis approach to bonding is the superposition of wave functions for each contributing canonical structure. Each atom has an octet. This formalism does not indicate that the molecule is resonating between the two extreme Lewis structures.
Use this condensed chemical structure to complete the table below CH2-CH3 The condensed chemical structure of p-diethylbenzene. According to the contributing structures each NO bond is an average. Number of carbon-hydrogen single C-H bonds.
Well the following resonance structures are of the phenolate ion which are correct. It has two equal NO bonds of 125 pm intermediate in length between a typical NO single bond 145 pm in hydroxylamine H 2 NOH and NO double bond 115 pm in nitronium ion ONO. We can describe the bonding in benzene using the two resonance structures but the actual electronic structure is an average of the two.
Draw a lewis structure of given molecule 2. Double-ended arrows are used to indicate that the structures are chemically equivalent. Dinitrogen monooxide or N_2O has three resonance structures out of which one is a major contributor and one is a minor contributor.
Resonance structures are described by using the double-headed arrow formalism. Zhang M Chemometrics to chemical modeling. P-Diethylbenzene - chemical information properties structures articles patents and more chemical data.
The actual structure is a superposition sum of the two wave functions. But the question then remains as to which oxygen should be involved in the double bond. We never really need to know the number of resonance structures.

Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance The Nmr Spectra Included
1 4 Diethylbenzene C10h14 Pubchem
1 2 Diethylbenzene C10h14 Pubchem

Chapter 13 Lecture Outline Prepared By Harpreet Malhotra
N N Diethylbenzenesulfonamide C10h15no2s Pubchem
P Diethylbenzene An Industrial Solvent Can Be Chegg Com
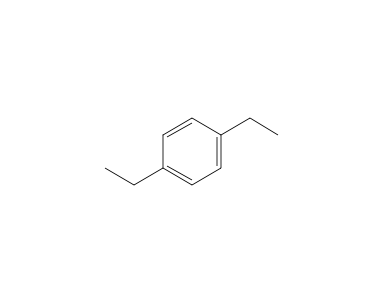
1 4 Diethylbenzene 1h Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase

Ethylbenzene Png Images Pngwing
P Diethylbenzene An Industrial Solvent Can Be Chegg Com

1 4 Diethylbenzene 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase
Ppt Benzene And Aromatic Compounds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 174763
1 4 Diethylbenzene C10h14 Pubchem
P Diethylbenzene An Industrial Solvent Can Be Chegg Com
Organic Chemistry Aromatic Compounds 22 Arenes

1 4 Diethylbenzene 13c Nmr Chemical Shifts Spectrabase

Chapter 12 Spectroscopy And Structure Determination Principles Of

Use This Condensed Chemical Structure To Complete The Chegg Com

Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance The Nmr Spectra Included
1 4 Diethylbenzene C10h14 Pubchem
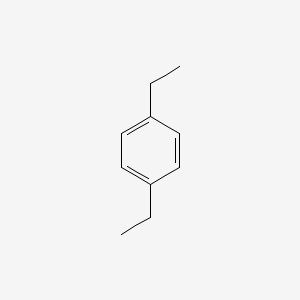

0 Comments